Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 |
Tags
- dynamic
- 재귀
- Tutorial
- 백준
- Algorithm
- Material
- 기초
- Programming
- guide
- w3school
- python
- 프로그래밍
- 문제풀이
- C#
- Unreal Engine 5
- parameter
- c++
- W3Schools
- github
- dfs
- loop
- 파이썬
- 시작해요 언리얼 2022
- DP
- Class
- UE5
- Basic
- 오류
- String
- Unity
Archives
- Today
- Total
행복한 개구리
C++ Classes - Polymorphism 본문

다형성
다형성이란 "여러 형질을 갖는다"는 의미입니다. 그리고 이것은 우리가 서로 상속하는 많은 클래스를 가질 때 나타납니다.
우리가 이전 챕터에서 특정했던 것처럼; 상속은 다른 클래스의 메서드와 속성을 상속하게 해줍니다. 다형성은 그 메서드들을 이용해 서로 다른 업무를 수행합니다. 이것은 우리가 또 다른 방식으로 단일 행동을 수행할 수 있습니다.
예를 들면, Animal 이라고 불리는 기반클래스는 animalSound() 라는 메서드를 가지고 있습니다. Animal의 파생클래스인 Pigs, Cats, Dogs, Birds가 있으며 그들은 그들 고유의 animal sound를 구현합니다.
예시
// 기반 클래스
class Animal {
public:
void animalSound() {
cout << "The animal makes a sound \n";
}
};
// 파생 클래스
class Pig : public Animal {
public:
void animalSound() {
cout << "The pig says: wee wee \n";
}
};
// 파생 클래스
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void animalSound() {
cout << "The dog says: bow wow \n";
}
};
이제 우리는 Pig 와 Dog 객체를 만들고 animalSound()에 재정의하는게 가능해졌습니다:
예시
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 기반 클래스
class Animal {
public:
void animalSound() {
cout << "The animal makes a sound \n";
}
};
// 파생 클래스
class Pig : public Animal {
public:
void animalSound() {
cout << "The pig says: wee wee \n";
}
};
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void animalSound() {
cout << "The dog says: bow wow \n";
}
};
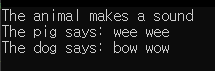
int main() {
Animal myAnimal;
Pig myPig;
Dog myDog;
myAnimal.animalSound();
myPig.animalSound();
myDog.animalSound();
return 0;
}
'C++ > 공부내용' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ Classes - Exceptions (0) | 2022.06.30 |
|---|---|
| C++ Classes - Files (0) | 2022.06.30 |
| C++ Classes - Inheritance / Access Specifiers (0) | 2022.06.29 |
| C++ Classes - Inheritance / Multiple Inheritance (0) | 2022.06.29 |
| C++ Classes - Inheritance / Multilevel Inheritance (0) | 2022.06.29 |




